Researchers at A*STAR’s Singapore Bioimaging Consortium (SBIC) have discovered that branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) in tumours can be targeted to prevent and treat cancer.
Together with collaborators from the United States and National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), they found that some cancers potently suppress the catabolism (breakdown) of BCAAs. This leads to BCAAs accumulating in tumours and activating a known pro-oncogenic pathway called mTOR. Researchers also found that dietary BCAA intake was directly linked to tumour development, suggesting that diets low in BCAAs could limit tumour progression and enhance overall survival.
In recent years, studies have shown that numerous metabolic pathways are altered in cancer cells. However, it has also been reported that many of the same metabolic pathways are altered in normal proliferating cells, suggesting they may simply be related to proliferation, rather than specific to cancer. The researchers designed a project to circumvent this problem by studying not only Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), the predominant form of liver cancer, but also healthy regenerating liver tissues. After identifying BCAA metabolism as a key pathway specific to liver cancer, they proceeded to find similar changes in stomach, colorectal, and kidney cancers, amongst others. Worldwide, cancer is the second leading cause of death, with stomach, colorectal and liver cancers accounting for some of the most common causes of cancer deaths[1].
SBIC’s findings are a result of six years of comprehensive preclinical and clinical research in collaboration with Duke University, the NCCS, and the University of Rhode Island. The research study tapped on SBIC’s multi-disciplinary capabilities and involved transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses of human tumours, cancer cell lines, and animal models of liver cancer and regeneration.
Suppression of BCAA Catabolism as a Driver of Liver Cancer Development and Progression
The research team led by Dr. Han Weiping, Deputy Director of SBIC and Head of the Laboratory of Metabolic Medicine (LMM), and Dr. Russell Ericksen, Research Scientist in LMM, first studied gene expression levels in matching tumour and non-tumour liver samples from HCC patients at NCCS, and validated their findings with data gathered from multiple independent HCC cohorts, such as The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The team found that the catabolism of BCAAs was not only suppressed in tumours when compared to adjacent normal tissue, but the degree of suppression correlated with tumour aggressiveness and disease progression. They also identified three BCAA catabolic enzymes – BCKDHA, ACADS, and ACADSB that were the best predictors of patient survival (Refer to Figure 1 of Annex A for details).
The changes in BCAA metabolism were confirmed by analysing metabolite and protein levels, as well as enzyme activity in the matching tumour and non-tumour liver samples. Using a new hyperpolarised magnetic resonance spectroscopy method developed by the SBIC researchers, enzyme activity in the livers of live subjects was monitored in real-time. This non-invasive technique could eventually be used in the clinical setting to screen patients for changes in BCAA catabolism.
By comprehensively analysing additional cancer subtypes profiled by TCGA, the investigators also found that reduced expression of BCAA catabolic enzymes correlated with tumour development, progression and aggressiveness, as well as patient survival in numerous other cancers. These associations were strongest in cancers of the colon and rectum, stomach, kidney and adrenal cortex. Regardless of cancer subtype, when the TCGA patients were analysed collectively as a pan-cancer cohort, those with higher tumour expression of BCKDHA, ACADS, and ACADSB lived significantly longer.
Dietary BCAA Intake Linked to Tumour Development and Growth
Given that BCAAs are essential amino acids – meaning they are absorbed from food rather than produced naturally in the body – the researchers also explored how dietary BCAA intake influenced tumour development and growth. In one study, the researchers used a common mouse model of liver cancer, and fed the mice diets with either normal or high levels of BCAAs. After five to eight months, the group of mice fed with high BCAA diets had a potent increase in tumour number and size. Of note, the same diet did not cause any changes in control mice that do not normally develop tumours, suggesting the effects were specific to cancer. Conversely, promoting the catabolism of BCAAs by administering a pharmacological compound, or feeding the mice a low BCAA diet limited tumour growth. These findings signal that BCAA accumulation regulates liver tumour development, and that dietary intervention could influence tumour progression and overall survival (Refer to Figure 2 of Annex A for details).
Finally, the researchers analysed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III cohort, which has detailed nutritional and medical information. In agreement with animal studies, this analysis suggested that high dietary intake of BCAA is also associated with a high overall cancer mortality risk in humans (Refer to Figure 3 in Annex A for details).
Dr. Han Weiping said, “The current study presents opportunities for the development of prevention and therapeutic intervention strategies to treat several common and deadly cancers. We hope to see that our study eventually leads to new drugs and therapies that benefit patients.”
“This important study by Dr. Han Weiping’s team is key in better understanding the role of the interesting cancer-driving metabolites, BCAAs – not only for liver cancer, but also potentially in other cancers. The finding that dietary BCAAs regulate cellular metabolism uncovers new factors in the cause of liver cancer, and potentially new drug targets,” said Associate Professor Toh Han Chong, Senior Consultant Medical Oncologist and Deputy Medical Director (Education), NCCS.
Moving forward, the team will work with NCCS to continue investigating the underlying mechanisms by which BCAAs regulate HCC, and to develop and test the efficacy of drug compounds that may lead to better treatment and outcomes for patients.
For more information on the research, please refer to the paper “Loss of BCAA catabolism during carcinogenesis enhances in mTORC1 activity and promotes tumor development and progression”, published online by peer-reviewed journal Cell Metabolism on 17 January 2019.
Link to online version: https://bit.ly/2FDjHdw
[1] Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
See the Full Release with Annex at: http://www.acnnewswire.com/clientreports/598/SBIC_1901.pdf
Annex A – Images, Graphs and Charts Used in SBIC’s Research Study
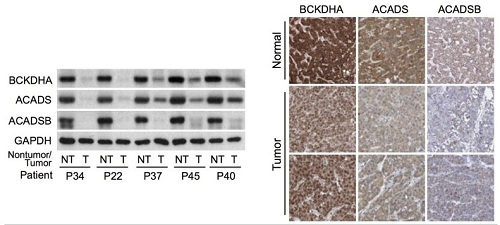
On the above is Western blot analysis on non-tumour (NT) and tumour (T) tissues from HCC patients enrolled at NCCS, showing a sharp decrease in expression of three important BCAA catabolic enzymes (The GAPDH enzyme was used as loading control). On the right are images of normal liver tissues or HCCs stained with antibodies for the three BCAA catabolic enzymes. The images were obtained from the Human Protein Atlas. Normal liver tissues typically have high expression (dark brown), while tumours have weak expression, confirming results from the NCCS cohort.
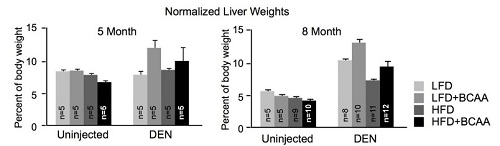
The two charts show the liver masses of mice at five month (left) and eight month (right) time points (normalised to the body weights of the mice). At both time points, mice which were introduced to diethylnitrosaine (DEN) – a compound which generates tumours from within an organism, and fed diets with high levels of BCAAs, had a greater tumour burden, as reflected by increased liver masses. This effect was consistent in diets containing either low or high levels of fat (LFD and HFD, respectively). Notably, the high BCAA diets did not substantially impact the healthy livers of uninjected mice.
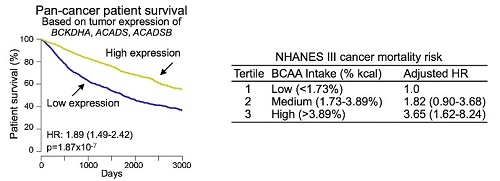
The above chart shows that patients with tumours that have high expression of the genes BCKDHA, ACADS and ACADSB live significantly longer than those with tumours that have low expression. The data was derived from the TCGA pan-cancer cohort of over 7,000 patients. The right chart shows the dietary analysis of the NHANES III cohort. It indicates that humans who have a high dietary intake of BCAA are more likely to develop and die from cancer.
About A*STAR’s Singapore Bioimaging Consortium (SBIC)
The Singapore Bioimaging Consortium (SBIC) under the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), is a leading preclinical bioimaging platform in the world. With a multidisciplinary team of biologists, physiologists, chemists, physicists, electrical/electronic engineers, computer scientists, and clinicians, SBIC investigates human diseases which are major public health issues using molecular physiology and advanced bioimaging tools, in a translational and pivotal mode with the medical community and industrial partners.
SBIC also works on strategic bioimaging projects, including the development of novel imaging probes. As a national consortium, SBIC aims to harness existing imaging expertise and capabilities in Singapore, bringing together substantial strengths in the physical sciences and engineering with those in the biomedical and clinical sciences. Through an array of focused collaborations and joint appointments, SBIC fosters and supports the growth of multidisciplinary research activities in the field of bioimaging across local research institutes, universities and hospitals, in order to accelerate the development of biomedical research discoveries. SBIC has a unique capacity to promote rapid transfers of results in animal and human imaging research into the clinical environment, to the immediate benefit of patients. It also ensures the development of financially sound and sustainable contractual research with industrial partners (pharma, food & nutrition, and personal care). SBIC currently operates five joint laboratories with industrial partners under the form of public-private partnerships. For more information about SBIC, please visitwww.sbic.a-star.edu.sg.
About the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) is Singapore’s lead public sector agency that spearheads economic oriented research to advance scientific discovery and develop innovative technology. Through open innovation, we collaborate with our partners in both the public and private sectors to benefit society.
As a Science and Technology Organisation, A*STAR bridges the gap between academia and industry. Our research creates economic growth and jobs for Singapore, and enhances lives by contributing to societal benefits such as improving outcomes in healthcare, urban living, and sustainability.
We play a key role in nurturing and developing a diversity of talent and leaders in our Agency and research entities, the wider research community and industry. A*STAR’s R&D activities span biomedical sciences and physical sciences and engineering, with research entities primarily located in Biopolis and Fusionopolis. For ongoing news, visit www.a-star.edu.sg