There are many reasons for pharma and biotech companies for a technology transfer: Some need a back-up strategy for risk management to provide an adequate market supply for the patient.
For others, there may be a lack of appropriate resources/capacity for process optimization, change in packaging, different regulatory requirements or a change in the product life cycle management.

Further, a technology transfer is also necessary for scale-up or when moving a drug product from one commercial aseptic manufacturing facility to another with the need for larger batch size. Every technology transfer is high-risk, involving strict regulatory requirements and adherence to detail. An experienced clinical supply partner is critical in this challenging manufacturing process.
Before you start, conduct a Gap- and Risk analysis
Technology transfer is a complex and time-consuming undertaking for a CDMO, especially since multiple partners and sites are involved. Any existing knowledge previously gained from the development of the drug product including experiences of the manufacturing process and the entire environment should be known and must be identified, including
• the filing strategy,
• critical quality attributes (CQAs) that must be controlled and tested to achieve the target product profile (TPP),
• logistical procedures,
• analytica lmethods,
• equipment, materials and instructions.

Further, a proper documentation of data and information and the application of risk management elements according to the ICH Q8 guideline is similarly important for success.
Then, a combination of gap and risk analysis must be undertaken to assist in identifying and evaluating any knowledge gained from the development and manufacturing process of the drug and to assess the risk of any identified differences between transfer sites.

Potential risks to the product quality attributes, process and regulatory consequences must be then identified and possibly new process parameters established. At the receiving site, process design is necessary to accommodate the known and newly identified critical process parameters (CPPs) to meet critical quality attributes. Process qualification to verify constant quality, the establishment of a control strategy at the receiving site, and the identification and controlling of sources of variability in material and processes are also necessary.
With technology transfer, expertise is essential
As with any complex and intricate action involving high-quality GMP-conforming clinical manufacturing, detailed planning and reliable execution within time and budget is required. Numerous steps and challenges including strict regulatory requirements and extreme attention to detail are critical for a successful transfer. Because multiple partners and sites are involved, the best approach is often working with a skilled partner with considerable experience in transferring aseptic manufacturing processes, necessary systems, routine and management skills.
The choice of a skilled outsourcing partner is critical to ensuring the successful transfer of a drug product. Because every transfer is associated with its own set of issues, its complexities should never be underestimated. Be certain that the company offers a detailed gap analysis and has significant experience and analytical methods for process design and development. The execution of Risk Analysis requires experts to identify the relevant degree of detail. Its success is largely dependent on the skill and performance of individuals assigned to the project as well as the experience of the transferring team. Be certain that the appropriate individuals are involved from the start.
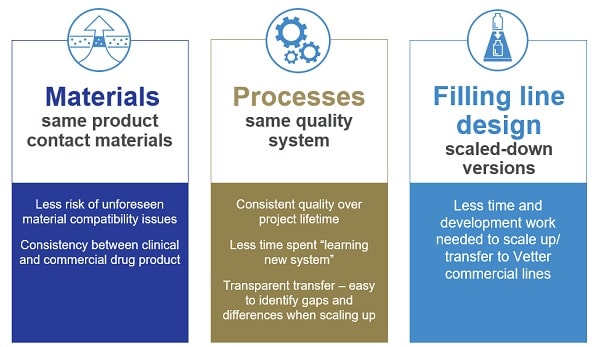
Vetter’s estalished transfer concept
Vetter offers a strong concept transferring clinical manufacturing in Chicago, USA, to commercial fill & finish facilities in Ravensburg, Germany: